Center drills are crucial tools in machining, primarily used to create center holes in workpieces to ensure the accuracy of subsequent operations. Depending on the specific application, center drills come in various shapes, each with unique functions. Below are some common types of center drills and their specific uses:
1. Common Shapes of Center Drills
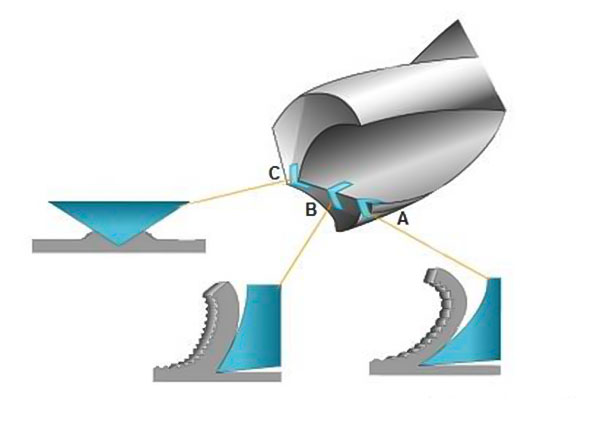
Type A Center Drill
This is a standard center drill with symmetrical cutting edges on both ends. Its primary function is to create a precise center hole in the workpiece, which serves as a reference point for further operations such as drilling, turning, or milling. The 60° taper angle of Type A center drills is suitable for most metals and common materials.
Type B Center Drill
The Type B center drill has a tapered cutting edge on one end and a stepped design with a guide hole on the other. It is specifically designed for applications requiring precise positioning and stable guiding. The outer 120° tapered surface (also known as the protective taper) helps protect the edge of the 60° taper from damage, extending the workpiece’s service life.
Type R Center Drill
The cutting edge of the R-type center drill has a curved design, making it suitable for hard materials like stainless steel and high-strength alloys. The curved edge increases the tool's strength and reduces wear during cutting, prolonging the drill’s lifespan and ensuring high-precision center holes.
Type C Center Drill
Type C center drills feature larger-diameter guide holes, making them ideal for deep hole drilling. The guide hole enhances the stability of subsequent cutting tools, ensuring better concentricity and accuracy during the machining process.
Chamfer Center Drill
This type of center drill is specifically designed for chamfering operations. It creates smooth chamfered edges on the workpiece, eliminating burrs and reducing damage to the hole's edge. Chamfer center drills are ideal for pre-processing before finishing, significantly improving the quality of hole machining.
2. Coordination Between Center Hole Taper Angle and Center Tip Taper Angle
In machining, the taper angle of the center hole and the taper angle of the center tip must be precisely matched to ensure the workpiece remains stable during the process. This prevents workpiece misalignment or surface damage due to angle mismatches. The most common center hole taper angle is 60°, which is commonly paired with a 60° center tip for several key reasons:
Machining Precision: The 60° taper on both the center hole and tip ensures concentricity, reducing the chance of errors caused by misalignment.
Operational Stability: Matching the taper angle between the center tip and the center hole prevents wobbling or dislodging during machining, ensuring a smooth process.
Protective Function: The 120° protective taper, such as that found on Type B center drills, helps safeguard the outer edge of the center hole, preventing damage during rough machining or handling.
3. Classification of Center Holes
Based on application and machining requirements, center holes can be classified into the following categories:
Standard Center Holes
These are the most common types, typically featuring a 60° taper, and are suitable for most turning, milling, and other general operations that require accurate positioning and support.
Center Holes with Protective Taper
As created by Type B center drills, these center holes feature an outer 120° protective taper. This design is intended to protect the outer edge of the center hole from damage during rough handling or machining.
Threaded Center Holes
For high-precision applications where strong holding is needed, threaded center holes are used. These work in combination with threaded center tips to provide additional support and stability during machining.
Deep Center Holes
These center holes are deeper and feature larger guide holes, used mainly in deep hole drilling or when working with large-diameter workpieces that require enhanced support.
OEM Capability
 We like to do design according to all the customers' requirements, or offer them our new designs. With strong OEM/ODM capabilities, we can fill your sourcing demands.
We like to do design according to all the customers' requirements, or offer them our new designs. With strong OEM/ODM capabilities, we can fill your sourcing demands. Categories
| HSS-PM Taps | HSSE-M42 Taps |
| HSSE / HSS Taps | Spiral Flute Taps |
| Straight Flute Taps | Spiral Point Taps |
| Multi-function Taps |
| Solid Carbide Drill Bits | Twist Drill Bits |
| Center Drill Bits | Indexable U Drills |
| Flat-end Milling Cutter | Ball Nose End Mills |

