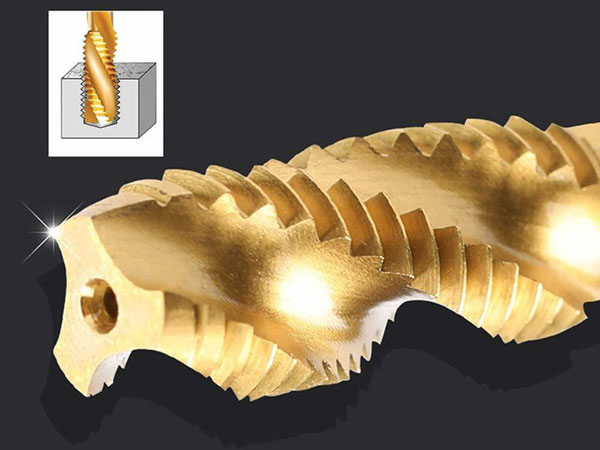
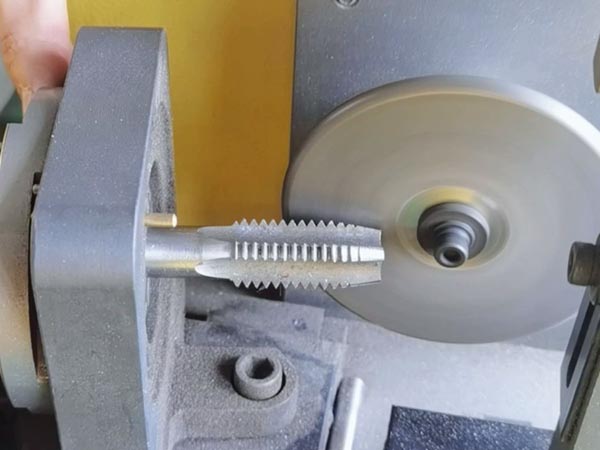
This article examines tap applications in materials like carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum, titanium alloys, cast iron, and composites. It covers material properties, recommended tap materials, coatings, industrial uses, and machining tips to enhance threading quality and efficiency.
View Article